This is a sponsored guest post.
If you have lung cancer, you may not have any symptoms until the cancer has metastasized and spread to other areas of your body. Even if you do have symptoms, it will be difficult to tell if lung cancer is behind them because in most cases the symptoms you experience will be the same as many other lung-related conditions.
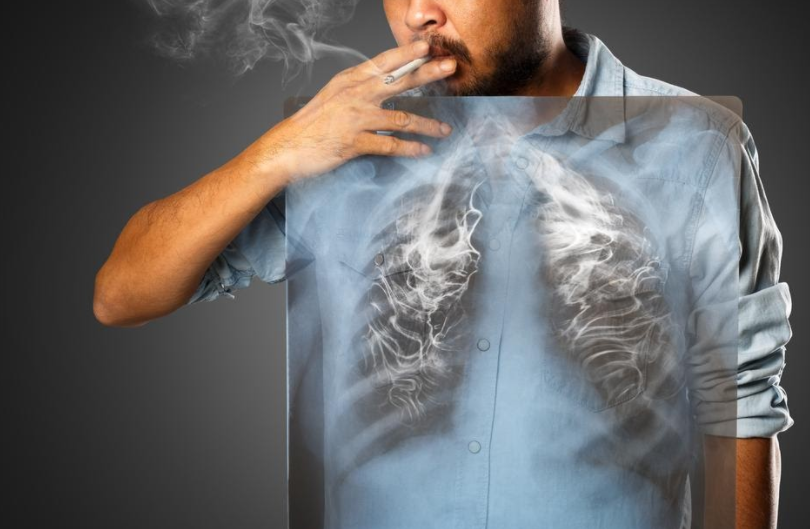
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should consult icrmc.org and get them checked out as soon as possible. Chances are the symptoms will be caused by something other than lung cancer.
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Wheezing
- Persistent cough
- Worsening cough
- Cough with rust-colored phlegm
- Recurring bronchitis
- Recurring pneumonia
Once lung cancer has spread, you will experience different symptoms that could include changes to your nervous system and pain in your bones. If your cancer has spread to the liver you may experience jaundice. If it’s spread to your brain, you may have dizziness and seizures. In the lymph nodes, it may cause swelling.
Causes of Lung Cancer
Although the above symptoms are unlikely to be lung cancer, if you’ve been exposed to any of the following carcinogens your odds of developing the condition may be higher.
Smoking
There are many carcinogens in cigarettes, and these damage your lungs when inhaled. Approximately 90% of lung cancer cases and 80% of all lung cancer deaths are caused by smoking, making this the leading cause of this deadly disease. Heavy smokers are especially at risk, with 24.4% of males and 18.5% 0f women who smoke heavily developing lung cancer.
Those who are currently smokers but don’t smoke heavily won’t fare much better, with 15.9% of males and 9.5% of females developing lung cancer. Quitting smoking now can lower your risk, with 5.5% of men and 2.6% of women who are former smokers developing lung cancer.
Secondhand Smoke
Even if you’ve never smoked, exposure to secondhand smoke can still cause you to develop lung cancer. In fact, it increases your risk by 20% to 30%. Secondhand smoke causes 7,300 lung cancer deaths per year, and there is no safe level of secondhand smoke exposure.
Radon
Approximately 15,000 to 22,000 people die from lung cancer caused by radon in the United States each year. Radon causes lung cancer when tiny radioactive alpha particles are inhaled into the lungs and cause structural damage to the lungs’ surface and basal epithelial cells, which are the cells that line the lungs.
Air Pollution
The air we breathe is filled with toxins like chemicals, dust, and smoke. When inhaled, these can cause cancer. Air pollution causes as many as 2% of all cases of lung cancer, and the more polluted air you inhale, the higher your risk. Researchers have also speculated that air pollution may cause changes in your DNA that make you more susceptible to developing lung cancer.
Asbestos
The most deadly type is pleural mesothelioma, a rare form of lung cancer that has no cure and has a 100% fatality rate. This type of lung cancer occurs when asbestos particles are inhaled and settle in your mesothelium, which is the thin tissue that surrounds your lungs. This causes tumors that grow and spread.
Approximately 4-12% of lung cancers are related to workplace exposure.If you’ve been diagnosed with lung cancer and you were exposed to asbestos at work, with an attorney’s help you may be able to get compensation that will help you cover your expenses.
Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you have any concerns about symptoms you are experiencing, especially if you’ve been exposed to any of these known causes of lung cancer. Your symptoms may be caused by another condition that is more easily treatable. And if it is lung cancer, early treatment can improve your odds of recovering.