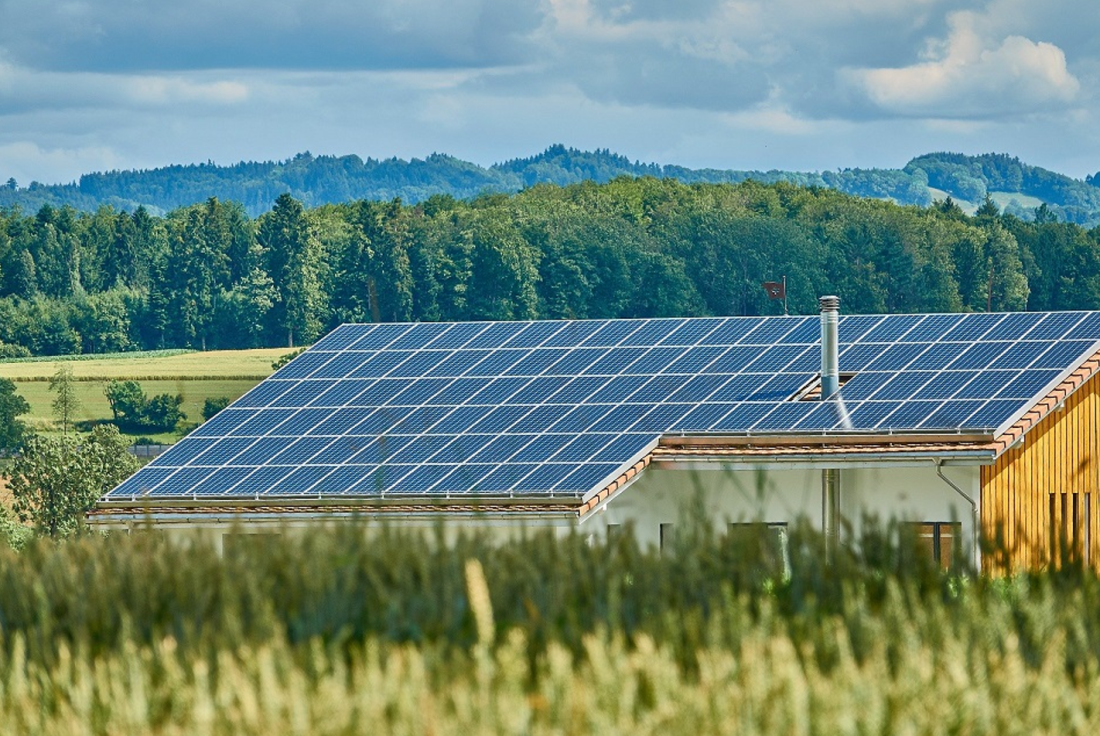
Solar power is simply described as the energy we generate from the sun. Before going solar, it is vital to understand that the use of solar energy can be passive or active.

Passive solar refers to the direct use of the sun’s light or heat without harnessing devices such as solar panels, solar thermal generators or solar concentrators. Examples of passive uses of solar include:
- Dehydrating perishable food
- Drying clothes
- Natural lighting
- Farming
Active solar energy systems use intermediary devices to enhance or amplify the sun’s energy. The sun generates energy in the form of heat and light. As such, active solar energy devices fall into two categories, namely, Solar Thermal and Solar Photovoltaic systems.
- Solar thermal systems harness the sun’s heat energy for productive use. Examples of solar thermal systems are:
- Concentrated Solar Power
- Solar Water Heaters
- Solar Dryers and Dehydrators
- Solar Photovoltaic Systems are devices that capture the sun’s light energy through solar panels. Solar panels are made of materials that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Solar Photovoltaic or PV systems are the most common form of solar technology in commercial use today.
Brief History of Solar
There are reports of humans in the 7th Century BC using glass materials to harness solar power for lighting fires. Also, the Romans in the 3rd Century BC used mirrors to manipulate solar energy and light torches for religious ceremonies.
Between 1760 and 1820, there were reports of solar collectors being used to capture the sun’s heat for controlled cooking and operating heat engines. Yet, it was not until the 19th century that interest in the active use of solar energy began taking root. Several discoveries and inventions in the 1800s led to the development of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels in use today.
The solar PV revolution began with the discovery of the photovoltaic effect in 1839 by a young French Scientist called Edmond Becquerel. The photovoltaic effect explains how certain metals such as silicon can generate electric currents when exposed to sunlight.
In 1954, Bell Labs in the USA developed the world’s first operational PV solar cell. The cell could convert enough solar energy to operate electrical appliances. Its efficiency ranged from 4% to 11%.
The global oil crisis in the 1970s led to massive investment in energy sources that could reduce the world’s reliance on fossil fuels. These investments sparked the beginning of the global solar revolution.
Solar PV technology prices began to drop in the wake of the global oil crisis. Statistics show that solar electricity per watt dropped from USD 101.05 in 1975 to USD 0.61 in 2015. Current projections show that the overall solar panel cost will drop to USD 0.21 by 2040.
Factors to Consider When Going Solar In Australia
Making a shift to solar energy is a decision many people in Australia are considering. There are several benefits to going solar when you live down under. The more information you can gather about solar, the easier your decision will be. Below are four factors that will help you know if it is the right time to switch.
- Solar Irradiance
- Grid Reliability
- Solar Panel Cost
- Australian solar Incentives
Several other factors can contribute to your decision to go solar. Yet, understanding the basic factors listed above gives you a solid foundation for assessing solar viability in your region. Below is an elaboration of each of the above factors.
i. Solar Irradiance
Solar irradiance defines the amount of power received from the sun per unit area on the earth. Solar irradiance is measured as Watts per square metre (W/m2).
Australia is the continent with the highest measure of direct normal irradiance (DNI). As such, they are considered to have the best solar resources across the globe. Yet, due to the distribution of Australia’s population, a significant amount of the country’s solar potential is in the Northwest deserts.
Yet, the country’s solar potential is so high that installing solar panels in Melbourne, for example, will yield more power than several other parts of the world.
ii. Grid Reliability
Going solar often means reducing reliance on the electricity grid. In places where the price of electricity from the grid is lower than solar, you should consider the grid’s reliability. Frequent black or brownouts disrupt commercial productivity and comfort in residential homes. Strong winds, forest fires and electrical faults can also compromise the power you receive from the regional grid.
If you live or work in a region where the grid power supply is unreliable, you should consider switching to solar. Solar panels give you independence from the grid by providing a reliable power supply. In regions where the grid is unstable, you should consider combining your solar panels with backup power.
Solar batteries are among the best backup power solutions to use with your solar panel system. The 12V solar panels charge your batteries during the day so you can use the reserve power at night.
In regions where the grid is reliable, you can use the grid electricity in harmony with your solar panels. Homes with grid-tie solar panels in Sydney can sell excess power back to the grid during the day. Also, the grid acts as your backup power when the sun goes down.
iii. Solar Panel Cost
The price of solar per watt vs conventional grid electricity is the main factor for most people. Saving money is attractive for businesses and homes alike. The price of solar panels is at an all-time low and going solar can even save on your electricity bills. Current statistics show that solar panels Sydney reduce your bills per kW significantly.
iv. Australian Solar Incentives
Despite the low price of solar panels, the high investment barrier prevents many people from going solar. The Australian government has established various incentives to help people overcome the initial cost of solar panels. Below is a list of government incentives you can benefit from in Australia.
- Federal Government Energy Rebates
- Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES)
- Large-scale Renewable Energy Target (LRET)
- Next Generation Energy Storage Grants
- Queensland solar and Battery Rebate
- Victoria solar Rebates
- State Feed-in Tariffs
All things considered, your decision to go solar comes down to your personal inclinations. If you desire to go green and save the environment, then the price of solar may not hinder your move. Yet, understanding the extra benefits of solar panels Australia may accelerate your decision.